
MELASMA


What is
MELASMA
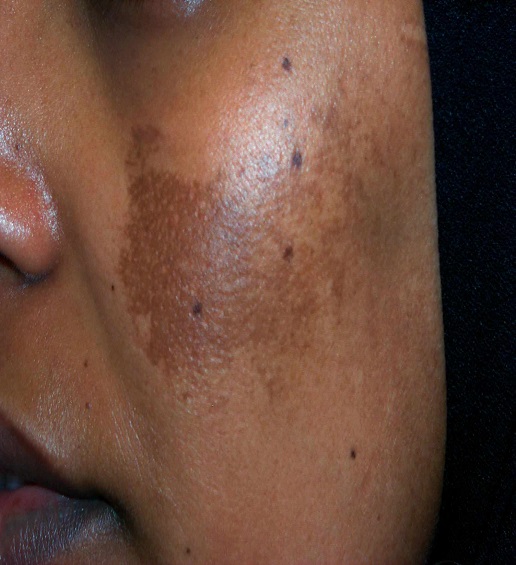
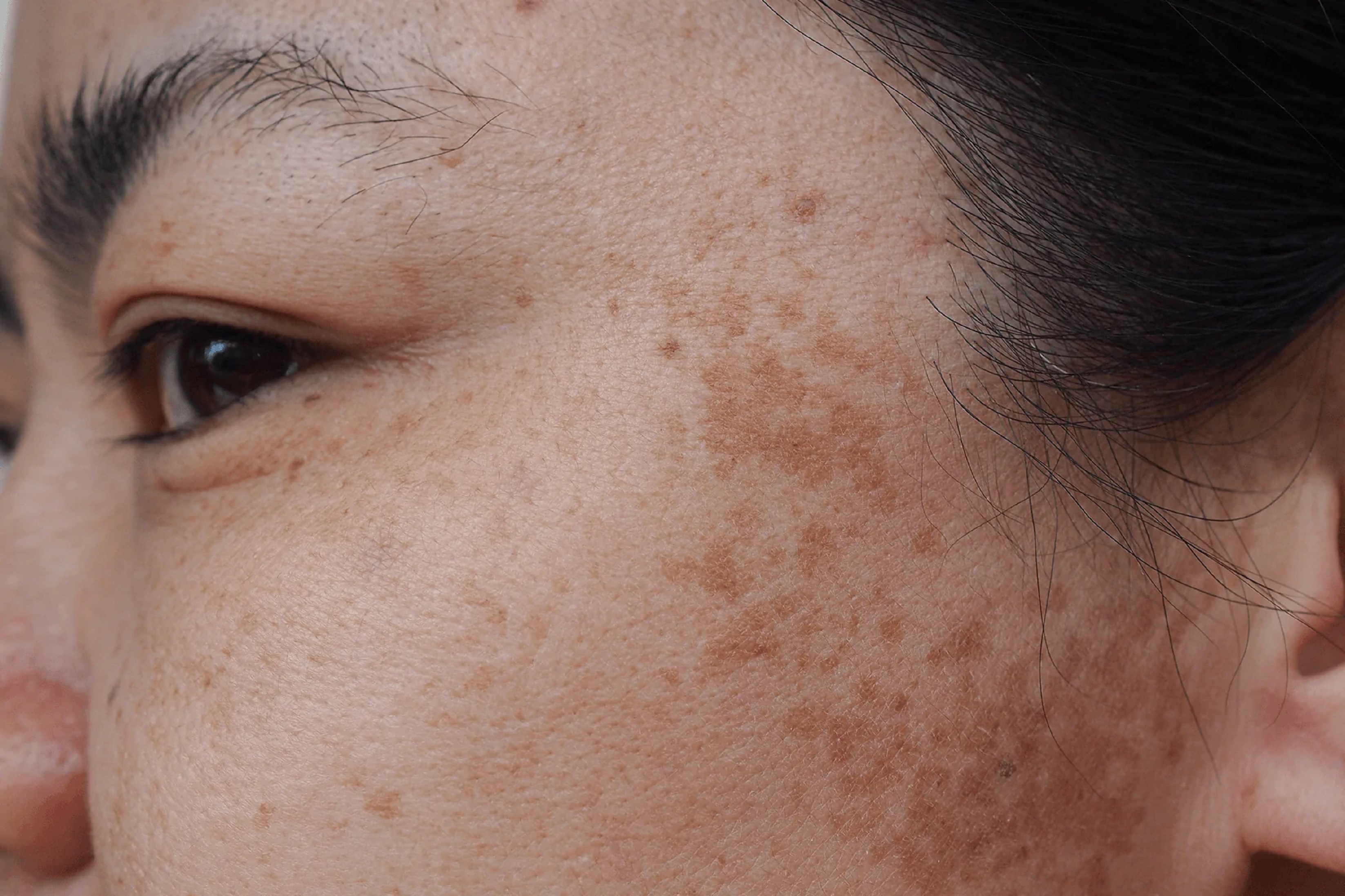
Melasma is a common skin condition in which brown patches appear on the skin. Melasma most often affects the skin on the face. It can also develop on the forearms and neck.

CAUSES
Melasma can be due to hormonal changes during pregnancy or from sun exposure. Women are much more likely than men to develop this condition.
In women, melasma often fades on its own after pregnancy or after an affected woman stops taking contraceptive pills.
Being out in the sun for too long and too often also puts you at risk for this condition. Melasma is common in people who live in tropical climates. People who have darker skin are also more likely to get it.

Our Treatments
Treatments for MELASMA
Most people with melasma do not need treatment. Melasma may fade away slowly if you stop taking birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy. If melasma appeared while you were pregnant, it may go away a few months after you have the baby. If melasma doesn’t fade or it bothers you, it can be treated. Skin lightening creams contains hydroquinone can help lasting Melasma. Creams that combine hydroquinone with kojic acid, azelaic acid, tretinoin, corticosteroids, or glycolic acid can also treat melasma. In some cases, your doctor may recommend a chemical peel, microdermabrasion, or laser treatment to help lighten the dark patches.
Our Services
Contact
-
#110, Rd Number 71, Jubilee Hills,
Hyderabad, Telangana 500033 - contact@stratumclinic.co.in
- +91 88802 82930